1. Introduction to Pyraminds
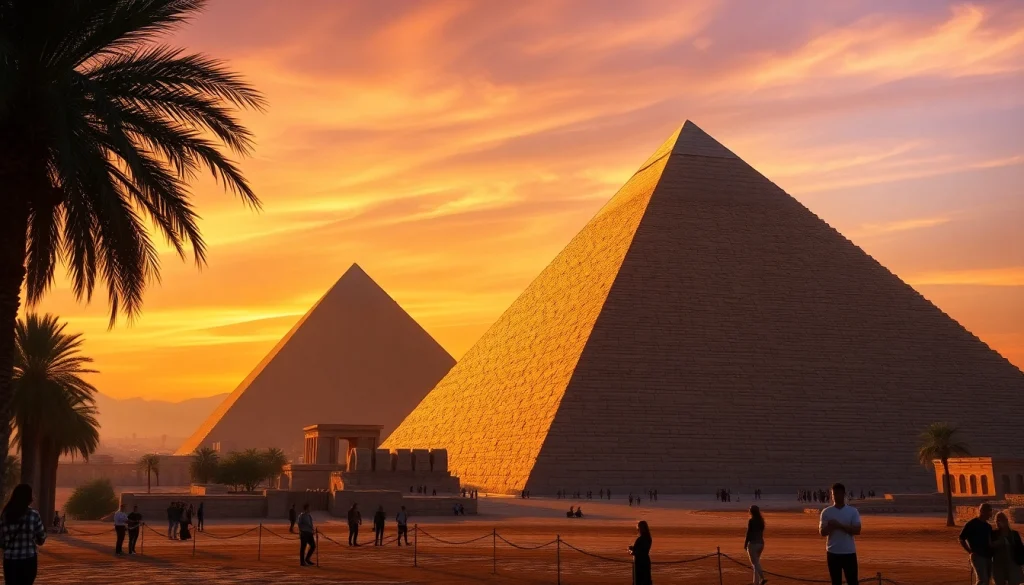
The world is fascinated by pyramid structures, particularly those erected in ancient Egypt. These monumental edifices, known as piraminds, possess an awe-inspiring presence that has captivated archaeologists, historians, and tourists alike. From their breath-taking architecture to their deep-rooted cultural significance, pyramids serve as a vital connection to our past. This article aims to delve deeply into the nature of piraminds, their architectural grandeur, cultural relevance, modern discoveries, and address frequently asked questions about these iconic structures.
1.1 What are the Pyraminds?
Pyramids are architectural structures characterized by a square or triangular base and converging sides that meet at an apex. These iconic formations serve various purposes throughout history, primarily as monumental tombs for dignitaries and nobility in ancient civilizations. The most notable examples, particularly from ancient Egypt, were constructed during the Old and Middle Kingdoms as burial sites for pharaohs, representing the spiritual journey into the afterlife.
1.2 Historical Significance of Pyraminds
The historical significance of pyramids transcends their physical form. They symbolize not only architectural brilliance but also reflect the socio-political and religious ideologies of the times in which they were built. The pyramids of Egypt were integral in the belief system surrounding the afterlife, serving as magnificent tombs that enabled the deceased pharaohs to ascend to the heavens and join the gods. This intertwining of architecture and spirituality is a key reason behind the enduring fascination with piraminds.
1.3 Overview of Pyramid Structures
Pyramid structures can be classified into several categories based on their design and construction methods. The most prominent types include the step pyramid, characterized by a series of stacked levels, and the true pyramid, known for its smooth, angled sides. Egyptian pyramids, particularly those on the Giza Plateau, represent the epitome of pyramid structures. Other cultures, including the Nubians and the Aztecs, also constructed pyramids, albeit with different architectural styles and purposes.
2. The Architecture of Pyraminds
The construction of piraminds is a testament to human ingenuity and engineering acumen. Every aspect of their design reflects an understanding of not only aesthetics but also structural integrity, allowing these massive edifices to endure for millennia.
2.1 Key Features of Pyraminds
- Base Structure: Most pyramids feature a square or rectangular base, establishing a solid foundation for the rest of the structure.
- Sloping Sides: The angled sides of the pyramids symbolize the rays of the sun, guiding the pharaoh’s spirit towards the heavens.
- Internal Chambers: Many pyramids contain intricate interior designs, including burial chambers and tunnels that reflect the burial customs of the time.
- Tomb Robbery Precautions: Features such as hidden chambers and complex passageways were employed to deter thieves from accessing the tombs.
2.2 The Construction Techniques Used
The construction of pyramids involved advanced engineering techniques. Workers employed a combination of manpower, simple tools, and architectural knowledge. Recent studies suggest that ramps, levers, and sledges facilitated the transportation of massive stone blocks from quarries to construction sites. Additionally, community labor systems allowed for the mobilization of large groups, showcasing the organization and commitment of ancient Egyptian society.
2.3 Variations in Pyramid Design
Not all pyramids look alike. Variations in design can be attributed to cultural, geographic, and temporal factors. For instance, while the classic Egyptian pyramids are well-known for their smooth, triangular faces, the step pyramids of the early dynastic period exhibit tiers that give them a stepped appearance. Moreover, other cultures, like the Mesoamerican civilizations, adopted pyramid building but integrated their own symbolic meanings and shapes, leading to unique architectural forms.
3. The Cultural Impact of Pyraminds
Pyramids extend beyond mere physical structures; they are cultural emblems that have stirred the human imagination for centuries. Their presence in myths, legends, and modern media underscores their significance.
3.1 Pyramids in Popular Culture
In modern times, pyramids have permeated popular culture, appearing in films, literature, and art. The mystique surrounding piraminds often fuels intrigue in conspiracy theories, ancient aliens, and paranormal activities, contributing to their portrayal as enigmatic symbols of forgotten knowledge. Iconic films, documentaries, and novels delve into the mysteries of these ancient structures, reinforcing their status as cultural landmarks.
3.2 Pyramids and Ancient Egyptian Religion
Pyramids are closely intertwined with the religious beliefs of ancient Egyptians. These structures served as a bridge between the earthly realm and the divine. The Pharaohs were viewed as deities on earth, and the construction of a pyramid was a significant part of their divine duty. The architectural features of the pyramids—their orientation, shape, and internal chambers—embodied religious symbolism that was essential for the transition into the afterlife.
3.3 Myths and Legends Surrounding Pyraminds
The aura of mystery surrounding piraminds has led to countless myths and legends. Stories of hidden treasures, curses, and the supernatural have emerged over time. One famous legend includes the belief that the Great Pyramid of Giza was built by extraterrestrial beings, highlighting humanity’s fascination with the unexplained. Such narratives enrich the cultural tapestry associated with pyramids and reflect our desire to understand the unknown.
4. Modern Discoveries Related to Pyraminds
With advances in technology and archaeological methods, new insights into the construction, purpose, and historical context of pyramids emerge regularly.
4.1 Recent Archaeological Findings
Recent excavations and studies have unveiled new chambers within existing pyramids and have confirmed the presence of extensive burial complexes. Modern techniques such as ground-penetrating radar have allowed archaeologists to uncover hidden structures and pathways. Such discoveries enhance our understanding of the labor organization and resources involved in pyramid construction, allowing us to appreciate the massive scale of these undertakings.
4.2 Innovations in Historical Research
Researchers are leveraging digital technologies and data analysis in pyramid studies. 3D modeling and simulations help visualize construction methods and evaluate structural integrity. Furthermore, interdisciplinary approaches combining archaeology, engineering, and anthropology provide a holistic perspective on piraminds, enabling scholars to better trace the interplay of culture, power, and engineering in ancient civilization.
4.3 Conservation Efforts for Pyraminds
As the impacts of time, tourism, and climate change threaten the integrity of pyramids, ongoing conservation efforts aim to preserve these historical monuments. Institutions and governments have developed restoration plans, utilizing scientific techniques to minimize erosive damage and enhance structural stability. Community involvement and educational initiatives also promote awareness about the cultural and historical value of piraminds, ensuring their legacy endures for generations to come.
5. Frequently Asked Questions About Pyraminds
5.1 How were the pyraminds built?
Pyramids were built using a combination of skilled labor, manual tools, and ingenious engineering techniques, including ramps, sledges, and levers, allowing for the transportation and placement of massive stone blocks.
5.2 What is the purpose of the pyraminds?
The primary purpose of pyramids was to serve as royal tombs for pharaohs, facilitating their journey to the afterlife, while also demonstrating the power and grandeur of their reign.
5.3 Are there pyraminds outside of Egypt?
Yes, pyramids exist in various cultures worldwide, including the Nubian pyramids in Sudan, Mesoamerican pyramids in Mexico, and the step pyramids in Central Asia, each with its cultural significance.
5.4 When were the famous pyraminds built?
The famous pyramids of Giza were constructed during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, roughly between 2580 and 2560 BCE, representing the peak of pyramid construction in ancient Egypt.
5.5 Can you enter the pyraminds today?
Many pyramids are accessible to visitors, allowing entry to burial chambers and passageways; however, some areas may be restricted for preservation purposes or due to structural concerns.